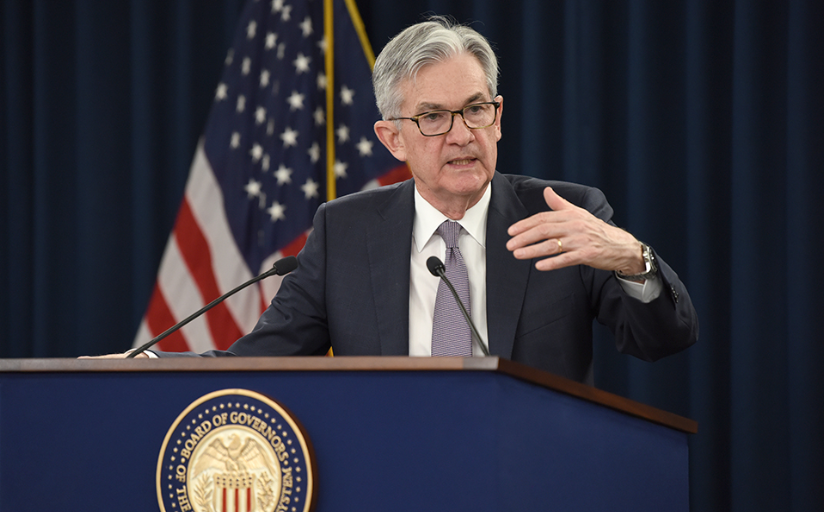
On September 20th, the latest minutes of the Federal Reserve's monetary policy meeting showed that the Federal Reserve had decided to slow down the pace of interest rate hikes in September and maintain the target range of the federal funds rate between 5.25% and 5.50%. Federal Reserve Chairman Powell stated at a press conference after the meeting that there is still a long way to go to control inflation, and the Federal Reserve will focus on the risks posed by high inflation to the United States in the coming period.
When will the Federal Reserve cut interest rates? In the latest lattice chart, the median expectation for the interest rate point at the end of 2024 in September is expected to reach 5.1%, while the expectation for the lattice chart in June is 4.6%. The median expectation for 2023 interest rates based on two dot matrix graphs is also 5.6%, which means that the number of interest rate cuts next year will be reduced from 4 to 2, leaving only 50 basis points. We do not expect any changes in interest rates this year, "said Jeffrey Roach, Chief Economist at LPL Financial. The discussion of possible interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve will emerge in the months leading up to 2024. Roach said when discussing the Federal Reserve's interest rate cut, it will be very important to look at holiday sales. If holiday sales are normal, it may occur in the second quarter of next year. According to Lu Zhe, Chief Economist of Debang Securities, the rise in oil prices and low base have driven the year-on-year rebound of CPI in August. Core inflation has continued to decline year-on-year, but non residential core service inflation has rebounded again or strengthened inflation stickiness. The year-on-year growth rate of CPI in the United States may be difficult to fall below 3% within the year. Lu Zhe believes that in the short term, the rebound in commodity prices and strikes by American automobile manufacturing workers may bring upward risks to inflation, or further increase the probability of interest rate hikes in November. In the medium to long term, the tail risk of inflation rising again due to energy, inventory replenishment, supply chain, and demand resilience means that there is still a distance to cut interest rates, and it is expected that the Federal Reserve will find it difficult to initiate rate cuts before the second half of 2024.
02 | The future direction of the Federal Reserve's monetary policy. After the Federal Reserve announced its latest resolution, Wall Street Journal reporter Nick Timiraos, who is regarded as the "Federal Reserve mouthpiece" and "New Federal Reserve News Agency," believes that Federal Reserve officials have hinted that they may raise interest rates again this year to curb inflation. He further pointed out that the median value of the lattice chart released this time shows that there will be two interest rate cuts next year. At the just held press conference, Powell first emphasized the important mission of the Federal Reserve to reduce inflation, stating that the FOMC is firmly committed to reducing the inflation rate to 2%. In terms of controlling inflation, the recent sustained rise in international oil prices has caused trouble for the Federal Reserve. Powell stated that sustained high energy prices will affect inflation expectations, and energy prices are very important to consumers. However, the Federal Reserve tends to ignore short-term fluctuations in energy prices. Regarding the interest rate path issue that the market is most concerned about, Powell stated that the Federal Reserve will be "cautious" in deciding whether to continue raising interest rates. Most policymakers believe that raising interest rates again this year is more likely to be appropriate. He added that the Federal Reserve's decisions will be based on data and risk assessment. The Federal Reserve has gone very far and very fast in raising interest rates, and higher interest rates are putting pressure on businesses and fixed investments. Regarding the timetable for interest rate cuts, Powell made it clear that no specific signal will be given at the moment, and we will have an opportunity to cut rates at an appropriate time. But there is too much uncertainty in lowering interest rates, and currently only speculation is that it will happen at some point in 2024, that's all.
03 | How long will the US dollar continue to strengthen? Since the Federal Reserve entered the interest rate hike cycle last year, the strong US dollar has been ongoing for over 16 months. The US dollar index has remained above 100, except for a brief drop below 100 in July this year. The sustained strength of the US dollar since mid year is related to the fact that inflation remains relatively high, leading to increased expectations of interest rate hikes. Although the US CPI inflation rate has continued to decline since reaching its peak of 9.1% in June last year, there have been signs of rebound in the recent July August period. The market originally believed that July this year was the peak of interest rate hikes, but currently inflation may rebound, and the pressure for the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates again before the end of the year is increasing. In addition to the expected increase in interest rates, the fundamentals of the US economy are also one of the factors affecting the trend of the US dollar. After the epidemic, the speed and magnitude of the growth rebound in the United States are relatively leading among major economies. In the second quarter of this year, GDP grew at an annual rate of 2.1%, accounting for approximately 70% of the US economy. Personal consumption expenditure increased by 1.7%. Powell also pointed out at this press conference that the US economic activity is stronger than everyone expected. GDP growth is driven by strong consumer spending, and currently, the balance sheets of American households and businesses are stronger than expected.
04 | Limited impact on A-shares, regardless of whether the Fed's interest rate hike this time or not, can only have a short-term impact on the economic market. If interest rates are raised, inflation in the United States will be suppressed, but it will also exacerbate the continued release of risks in the US banking industry. The US dollar index will emerge from a wave of high and then fall, putting short-term pressure on the domestic RMB exchange rate; If interest rate hikes are suspended, the pressure on the RMB exchange rate will be released, and there will be a downward trend in the US dollar index. Inflation pressure still exists, and a rebound in domestic asset prices will be beneficial for A-shares. In the medium to long term, it is still necessary to patiently wait for the consumer side to drive investment. Only when the volume can be released again can the market emerge from volatility and make a strong upward breakthrough. At present, the short-term liquidity of A-shares is still insufficient, and the leading indicators of the A-share market have reached a new low. The external factors have little impact on the A-share market and have an impact on the short-term trend. However, in the medium to long term, it still depends on the endogenous driving force of the A-share market, and insufficient capacity remains the main factor that makes it difficult for the market to strengthen in the short term.
05 Jingtai Viewpoint | "Soft Landing" Preserves Space for Further Rate hikes. The convening of the Federal Reserve's September interest rate meeting signifies that the rate hike has entered its final stage, but the market is still confused about the "implications" beyond the final stage. This undoubtedly increases the uncertainty in the market, and in order to reduce this uncertainty, we expect the Federal Reserve to release the following signals: 1. Recognize that the economic growth rate is stronger than expected. We expect that the meeting will significantly increase our forecast for year-on-year GDP growth in 2023, from 1% predicted in June to 1.8% in September. This matches the message conveyed in the September US Brown Book that the economy is growing moderately. 2. Implying that inflation has indeed slowed down. Due to the fact that the core inflation rate after quarterly adjustments has been below 0.3% month on month for three consecutive months, the Federal Reserve's meeting hinted at a benign slowdown in inflation by lowering its forecast for the core PCE for this year and next. 3. Increase expectations for a "soft landing" and reserve room for further interest rate hikes. Despite increasing economic expectations and slowing inflation, the Federal Reserve has not made any substantial adjustments to the 2023 chart and still retains the possibility of a rate hike. So before seeing more tightening data, there is still some room for the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates.