Article | Wang Zhixiao, Industry Researcher of Jingtai Capital

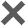
The aerospace industry can be subdivided into five sub-industries: missiles, rockets, satellites, spaceships and space probes. The current global market scale reaches hundreds of billions of dollars, and the long-term market scale reaches trillions of dollars. Development potential and imagination space huge.
Figure 1: Market size of each segment of the global and my country aerospace industry
▼
Source: NASA's Aerospace Report, "2018 World missile Briefing", American Satellite Industry Association, AVIC Securities and Finance Research Institute, compiled by Jingtai Capital
The aerospace industry has the characteristics of high technology, high investment, high risk, high benefit and long-term "four highs and one long", and my country's aerospace industry is quite different from foreign aerospace industries in terms of policy background and market demand. At present, the commercial application of my country's aerospace industry is mainly concentrated in the satellite industry and rocket industry. The main players are still state-owned assets, and private enterprises have entered late but developed rapidly.

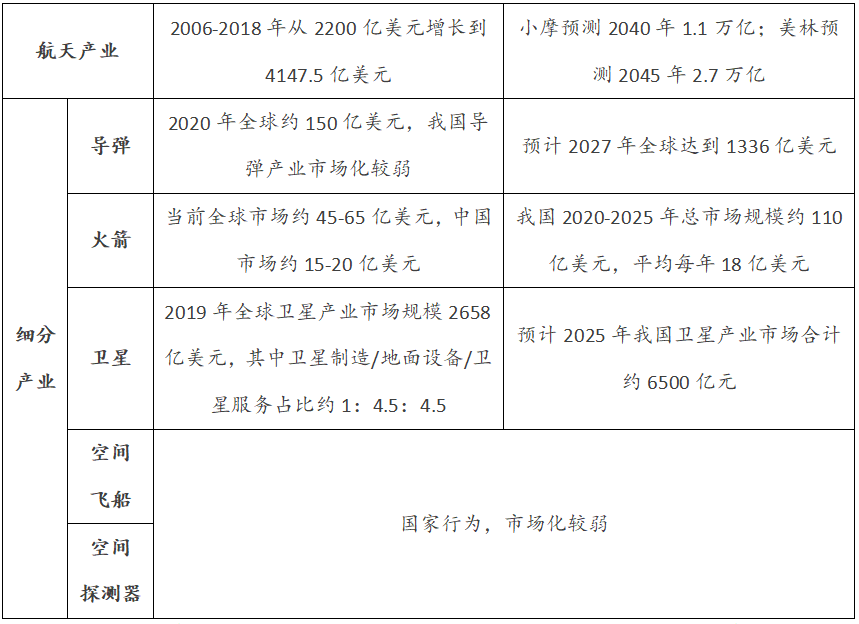
Overview of the launch vehicle system
According to the classification of rockets, there are mainly two types of launch vehicles and sounding rockets. The most widely used in the aerospace industry is the launch vehicle. The components of the launch vehicle mainly include the rocket body structure, propulsion system, control system, flight measurement and safety system, and additional systems.
Figure 2: Basic composition of the launch vehicle system
▼
Source: Launch Vehicle Engineering

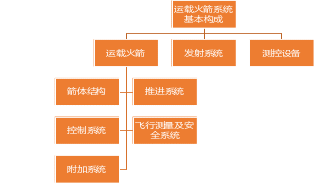
Launch vehicle industry chain
The commercial launch vehicle industry chain is divided into three parts: engineering development/machine manufacturing/test launch. The upstream of the industry chain is mainly for engineering research and development, which specifically involves the overall demonstration and design of the launch vehicle (including the overall design and sub-system design of the launch vehicle), simulation testing, and experimental parts. The middle reaches of the industrial chain mainly focus on the sample design, manufacturing and model assembly after the development and finalization of the launch vehicle, which can be further subdivided into the industrial chain according to the supporting processing and production of components, sub-system (component) integration, and model integration. The downstream of the industrial chain is mainly the flight test and application launch of the launch vehicle.
Chart 3: Launch Vehicle Industry Chain and Related Listed Companies
▼
Source: Wind, AVIC Securities Finance Research Institute
Almost all parts of the industrial chain are mainly participated by enterprises and institutions affiliated to Aerospace Science and Technology and Aerospace Science and Industry Group, and the proportion of private commercial rocket enterprises is still relatively low.

Market Status of Launch Vehicle Industry
Application Scenario 1: Satellite Launch. The current main downstream application market for launch vehicles is satellite launch. Although the number of satellite launches has grown rapidly due to the influence of networking and constellation, due to the increase in the proportion of microsatellites or small satellites, and the development trend of "one arrow with multiple satellites" for launch vehicles, the number of launches and market size are expected in the short and medium term. It will remain stable, the global market is 4.5-6.5 billion US dollars, and the Chinese market is 1.5-2 billion US dollars.
Chart 4: Global and my country's satellite launch market size (billion US dollars)
▼
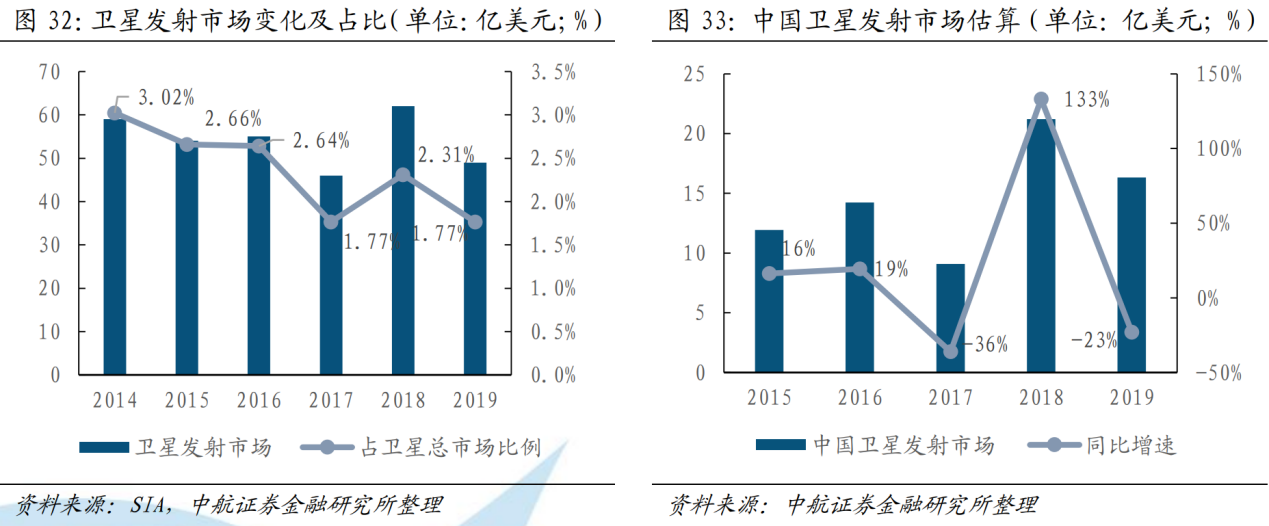
Data source: SIA, AVIC Securities Finance Research Institute
There is a large gap in rocket capacity in the short term, and there are opportunities in the commercial rocket market. As the satellite Internet is included in the national "new infrastructure" development category, the number of satellites launched in my country will exceed 10,000 in the next 5-10 years. Taking a constellation scale of 12,000 satellites, a single-satellite mass of 200kg, an orbital height of 700km, and a 7-year networking period as an example, to calculate the launch demand for networking, the average annual domestic market demand for rocket capacity will be about 343t/700km in the future. According to the rocket capacity statistics table, the total capacity of domestic rockets launching satellites in 2021 is about 140.4t/700km, which is a big gap.
Figure 5: Statistics of domestic rocket capacity for launching satellites in 2021
▼
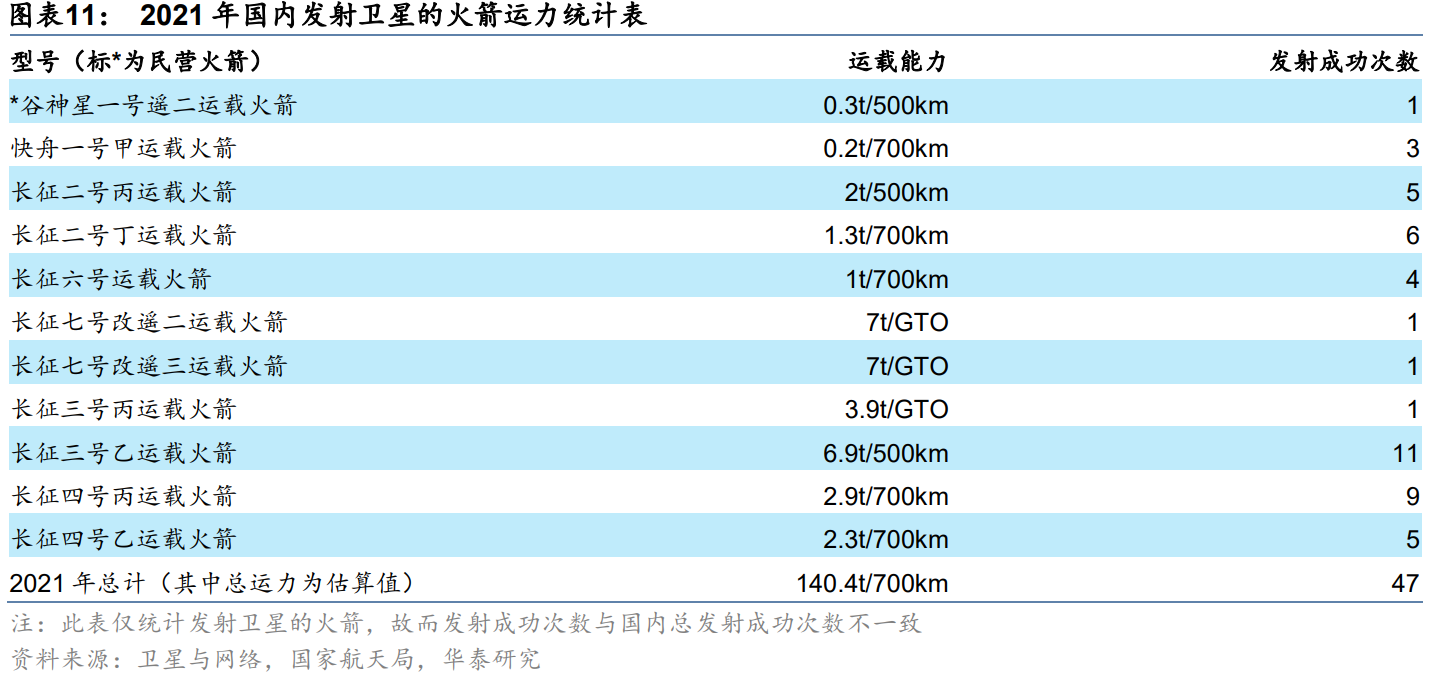
Source: Satellite and Network, National Space Administration, Huatai Research
The domestic commercial rocket launch industry has high costs and poor technical stability. At present, my country's commercial space launch industry is mainly based on the "Kaizhou" series of the rocket company affiliated to the Aerospace Science and Industry Group and the "Long March" series of the Aerospace Science and Technology Group. There are no reusable rocket models that have entered the application stage, and the launch cost is relatively high. At present, the domestic company's cost target of 10,000 US dollars/kg has not yet been achieved, while SpaceX's cost target has been lower than 3,000 US dollars/kg; launch stability and recovery technology are not yet mature.
Figure 6: Comparison of domestic and overseas commercial rocket companies
▼
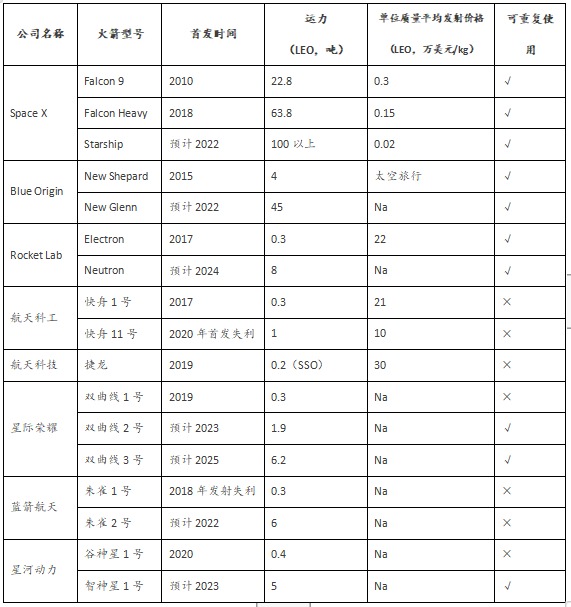
Source: Official website of each company
Application Scenario 2: Intercontinental spacecraft and space travel. According to Musk, with the commercial maturity of the SpaceX rocket BFR, the rocket can be used for intercontinental transportation. Intercontinental traffic has dropped from a level of 10 hours to less than 1 hour, which greatly facilitates the global transportation market. Companies such as Virgin Galactic in the United States are promoting space travel services with a single price of $250,000. Currently, about 600 people have booked the service, and nearly 10,000 people are willing to experience related products.
Application Scenario 3: Moon base and Mars immigration, etc. According to Musk, with the commercial maturity of the SpaceX rocket BFR, the rocket can be used for intercontinental transportation. Intercontinental traffic has dropped from a level of 10 hours to less than 1 hour, which greatly facilitates the global transportation market. Companies such as Virgin Galactic in the United States are promoting space travel services, but also for microgravity experimental applications and astronaut training applications. The single price is at the level of 250,000 US dollars. At present, about 600 people have booked the service, and there are nearly 600 people. Thousands of people are willing to experience related products. The company is still testing its spacecraft and has completed four tests. Five aircraft will enter service in 2023.

Technical Analysis of Launch Vehicles
The main technical indicators of the entire launch vehicle are the carrying capacity, orbit entry accuracy and reliability. Among them, the carrying capacity represents the weight of the payload that can be sent into the predetermined orbit; the orbit entry accuracy represents the actual orbit of the payload and the predetermined orbit. The deviation is an important indicator of the launch vehicle control system; reliability is an important indicator to measure the probability of failure during the working process of the rocket system. In the current process of commercial aerospace development, cost characteristics and rapid response characteristics (launch preparation time) have also become important core indicators.
1. The sub-system of the arrow body structure (material manufacturing and processing) is developing towards lightweight materials. The rocket body structure of the launch vehicle is the main body of the rocket. It mainly includes the fairing, the interstage section, the tail section and other sections, while the liquid launch vehicle also includes the propellant storage tank. At present, ordinary high-performance metal materials are still an important part of aerospace structural materials, but their applications are basically close to the limit of technology. With the urgent need for weight reduction of aerospace vehicles, lightweight structural materials with excellent mechanical properties, especially Lightweight structural materials represented by aluminum alloys, magnesium alloys, titanium alloys and composite materials have become a hot spot in aerospace research.
2. The propulsion system is developing towards large thrust, low cost, high reliability, and convenient use and maintenance. Among them, high reliability and low cost are the top priorities for the development of commercial rockets. The rocket propulsion system mainly includes three parts: the main power system, the auxiliary power system and the booster delivery system. The main power system, namely the engine system, is mainly analyzed here. At present, rocket motors can be divided into solid rocket motors and liquid rocket motors.
The fixed rocket has a short launch period and a fast response speed, which is more suitable for military modernization for rapid response and satellite supplementary network launch. Solid rockets do not have an advantage in launch costs, and the national team's technical reserves on solid rockets are far ahead. Medium and large solid commercial rockets are difficult to break through in the short term, and liquid rockets are the mainstream of commercial aerospace.
Liquid rockets have higher specific impulses and greater capacity advantages. Because the carrying capacity of trucks and roads in the transportation link limits the overall weight of solid rockets, which limits the carrying capacity of solid rockets, in addition, medium and large solid rockets also face many technical difficulties that are difficult to break through, such as large segmented docking. In comparison, liquid rockets Easier to achieve large thrust.
Figure 7: Comparison of solid and liquid fuel rockets
▼
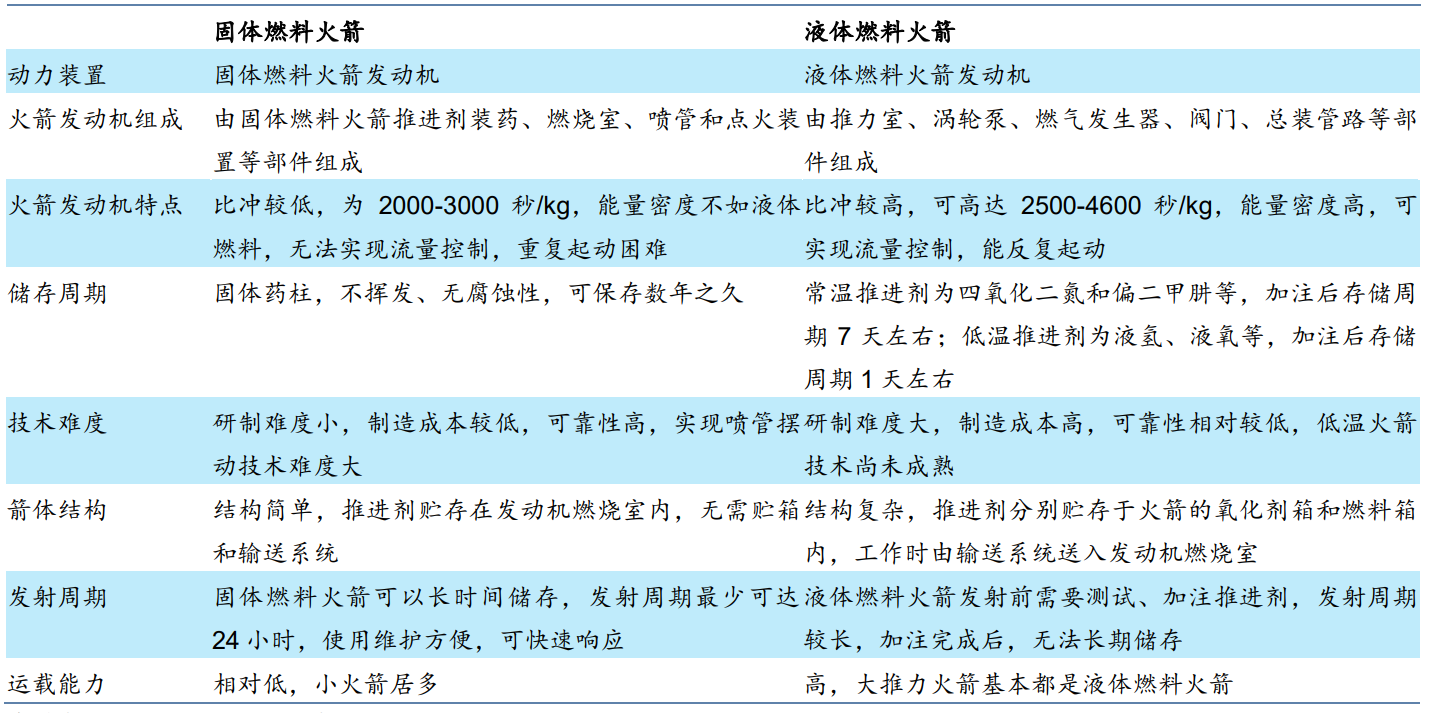
Source: Head Leopard Research Institute
The reusable technology of liquid rocket engines greatly reduces the cost, and the vertical recovery of the rocket and the reuse of the engine are expected to reduce the launch cost by one third. In the cost composition of a single-use launch vehicle, the engine accounts for about 54.3% of the total cost, the rocket body structure accounts for about 23.6% of the total cost, the electrical system accounts for about 8%, the valve pipeline and actuator account for about 8.1%, ignition, Pyrotechnics such as interstage separation accounted for about 5.3%, and propellant costs accounted for about 0.7%.
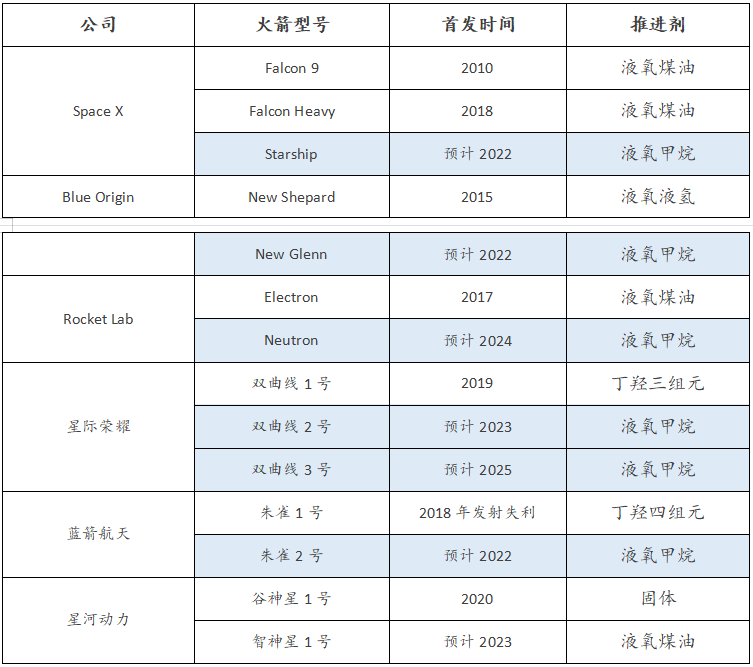
As the most valuable part of a rocket, rocket recycling is the only way for commercial aerospace to reduce costs. The three low-temperature propellants, liquid oxygen, liquid hydrogen, liquid oxygen methane and liquid oxygen kerosene, all meet the basic needs of the engine for repeated use. Among them, the comprehensive advantages of liquid oxygen and methane have become the development trend. Orbital flight precedent.
Figure 8: Major commercial rocket propellants
▼
The article is an analysis point of view of Jingtai and does not constitute investment advice. Please read it carefully.