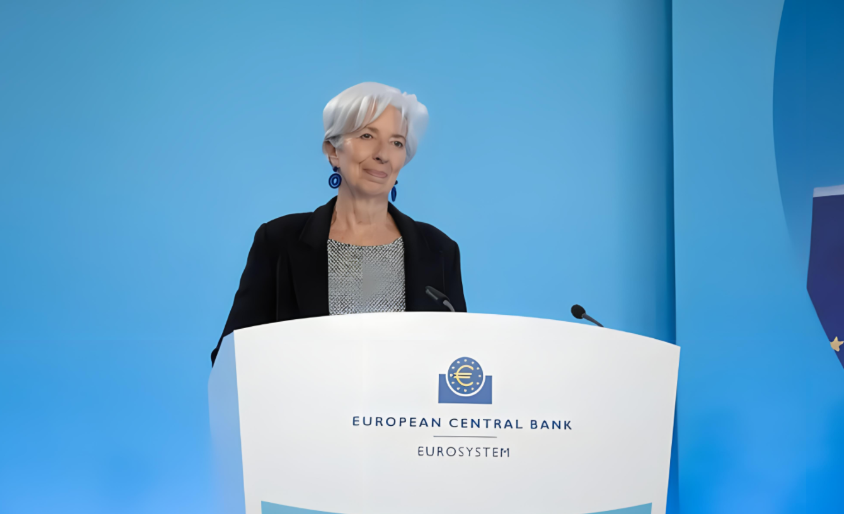
On March 7th, the European Central Bank announced its latest interest rate resolution, maintaining the three key interest rates unchanged for the fourth consecutive meeting. But the bank has lowered its inflation and growth expectations, which may pave the way for the first drop in the first half of this year. The European Central Bank announced that it will maintain the main refinancing rate, marginal lending rate, and deposit mechanism rate at 4.50%, 4.75%, and 4.00%, respectively, consistent with market expectations. This is the fourth consecutive time that the bank has chosen to maintain the current interest rate level, and the timing and magnitude of the first rate cut this year have become the focus of market attention.
01 | Lowering Economic Growth Forecast for 2024 and 2026 The Management Committee reiterated that the bank is determined to ensure that inflation returns to its mid-term target of 2% in a timely manner. Based on the current assessment, the members believe that maintaining the key interest rate for a sufficient period of time will make a significant contribution to achieving this goal. The management committee will continue to follow a data-driven approach to determine the level and duration of restrictions, especially with interest rate decisions based on the evaluation of inflation prospects based on upcoming economic and financial data, potential inflation dynamics, and monetary policy transmission strength. In the latest forecast, due to the decline in energy prices, Eurobank staff have lowered their inflation expectations for the eurozone. The latest figures are: the expected average inflation rate in 2024 is 2.3%, in 2025 it is 2.0%, and in 2026 it is 1.9%; In addition, the expected average core inflation rates for the past three years are 2.6%, 2.1%, and 2.0%, respectively. Financing conditions are restricted, and previous interest rate hikes continue to put pressure on demand, helping to lower inflation. Although most potential inflation indicators have further eased, price pressures remain high, partly due to strong wage growth. In terms of growth, due to the recent downturn in economic activity, staff have lowered their expected growth rate for 2024 to 0.6%. There may be a rebound in the next two years, and staff believe that with the support of consumption and investment, it will grow by 1.5% and 1.6% respectively in 2025 and 2026.
02 | Is the downward adjustment in preparation for interest rate cuts? As expected, the European Central Bank has lowered its inflation and economic growth forecast. Specifically, economic growth is expected to increase by 0.6% in 2024, compared to the previous expectation of 0.8% growth.
It is expected that GDP will grow by 1.5% in 2025, compared to the previous expectation of a growth of 1.5%.
It is expected that GDP will grow by 1.6% in 2026, compared to the previous estimate of a growth of 1.5%. Overall inflation: The expected inflation rate in 2024 is 2.3%, compared to the previous expectation of 2.7%.
The expected inflation rate for 2025 is 2%, compared to the previous expectation of 2.1%.
The expected inflation rate for 2026 is 1.9%, compared to the previous expectation of 1.9%. Core inflation: The expected core inflation rate in 2024 is 2.6%, compared to the previous expectation of 2.7%.
The core inflation rate is expected to be 2.1% in 2025, compared to the previous expectation of 2.3%.
The core inflation rate is expected to be 2% in 2026, compared to the previous expectation of 2.1%. In terms of inflation, the European Central Bank pointed out that in its latest economic forecast, inflation expectations have been lowered, especially in 2024, mainly reflecting a decline in energy prices. In terms of economic growth, the European Central Bank has stated that economic activity is expected to remain sluggish in the short term due to tight monetary policies restricting financing and suppressing demand.
03 Jingtai Opinion | The timing of the first rate cut in June and the magnitude of this year's rate cut may become the focus of market attention. European Central Bank President Lagarde said at a monetary policy press conference, "Policy makers have more confidence in achieving their goals, but confidence is not enough. We will also know more information in April, but we will know more in June. The European Central Bank will not make a commitment to the speed of future interest rate adjustments." She said that internal discussions have begun to ease restrictive positions and pointed out that action will not be taken until inflation reaches 2%. She also emphasized that the issue of interest rate cuts was not discussed at this meeting, and no commitment will be made to the speed of future interest rate adjustments. Due to the target inflation rate of 2% by 2025, Lagarde's remarks suggest that the European Central Bank may lower interest rates in June. Most investment banks, such as Deutsche Bank and Goldman Sachs, almost unanimously believe that the first rate cut will come in June, with economic resilience exceeding previous expectations and concerns about sustained high inflation supporting the European Central Bank's postponement of rate cuts. Jingtai expects the European Central Bank to maintain policy interest rates unchanged. Council members, including President Lagarde, have expressed greater optimism about inflation, but further progress is needed in the process of eliminating inflation in order to have confidence in timely and sustainable achievement of the European Central Bank's goals. Therefore, it is still expected that the European Central Bank will cut interest rates for the first time in June