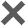
On August 11th, the People's Bank of China released financial statistics and social financing data for July 2023, which showed that the scale of new RMB loans and the increase in social financing scale in July were both relatively low, lower than market expectations. In the same month, China's RMB loans increased by 345.9 billion yuan, a year-on-year decrease of 349.8 billion yuan; The increase in social financing scale was 528.2 billion yuan, a decrease of 270.3 billion yuan compared to the same period last year. The financial data for July is significantly low, mainly due to short-term fluctuations caused by factors such as overdraft effects and delayed release of financing demand, which does not represent a change in the credit process. With the continuous increase in macroeconomic policy regulation, the phenomenon of credit downturn will not continue.
In July, both household deposits and loans decreased. In July, new short-term and long-term loans for residents decreased by 133.5 billion yuan and 67.2 billion yuan, respectively, with a year-on-year decrease of 106.6 billion yuan and 215.8 billion yuan, in sharp contrast to the high increase in household credit in June. Meanwhile, RMB deposits decreased by 1.12 trillion yuan in July, of which household deposits decreased by 809.3 billion yuan. The performance of new loans in July was significantly lower than expected, mainly due to the following reasons: firstly, the high increase in credit impulse in June had a certain overdraft effect on July's credit demand. This overdraft effect will significantly increase the fluctuation of new loan scale between months, which occurred multiple times in April, July, and October 2022. Secondly, despite the expected accumulation of stable growth policies in July, the implementation of incremental policies is limited, and the economic recovery efforts are still weak, especially with the further decline of the real estate market and weak credit demand from physical sectors such as enterprises and residents. The third issue is the implementation of interest rate cuts in June and the reduction of LPR quotations, which may have formed strong expectations for a downward trend in interest rates among loan entities. This may lead to some companies or residents delaying the release of financing needs, in order to wait for lower financing costs. For the decrease in long-term loans for residents, in addition to being dragged down by weak real estate sales, if combined with the decrease in residents' deposits (which decreased by 809.3 billion yuan in July, an increase of 471.3 billion yuan year-on-year), the impact of early mortgage repayment may also be significant. Behind this, or to some extent, it indicates that banks tend to encourage and arrange residents to make concentrated prepayment of mortgages at the beginning of the quarter in order to avoid the impact of early repayment and other disturbances on the quarterly assessment of deposits and loans.
02 | The increase in social financing scale significantly decreased compared to the same period last year. In the first seven months of this year, the cumulative increase in social financing scale was 22.08 trillion yuan, an increase of 206.9 billion yuan compared to the same period last year. From a monthly perspective, the increase in social financing scale in July decreased by 3.7 trillion yuan compared to the previous month, with a year-on-year decrease of 270.3 billion yuan. The increase in social financing scale is mainly affected by the significant decrease in the month on month and year-on-year increase in RMB loans invested in the real economy. In addition, government bond financing increased less month on month in July, mainly because of the increased pressure on the maturity of treasury bond and the low guiding interest rate for local bond issuance under the expectation of downward interest rate, while investors expected that the supply of subsequent local bonds would be increased, thus suppressing the primary subscription sentiment, which led to a large delay in the issuance of local bonds in July. Although the growth rate of social finance slowed down in July, the research report pointed out that looking forward, the growth rate of social finance is expected to rebound. The down payment ratio and loan interest rate for the first home are expected to decrease, and the leverage window for real estate loans is expected to restart; The issuance of government bonds in the third quarter is also expected to accelerate, supporting the investment of infrastructure loans. It is expected that the growth rate of social finance and loans will rebound to around 10% by the end of the year.
03 | The issuance of special bonds may accelerate the expansion of July corporate bonds compared to last month, mainly due to the low base caused by last year's real estate turmoil, and the overall low net financing of corporate bonds. The financing of government bonds in July remained basically unchanged from last year's low base, or was related to the slower pace of issuance due to the increase in fiscal deposits. The Politburo meeting called for the acceleration of the issuance of special bonds, and it is expected that there will be a supply peak from August to September, which will drive a significant rebound in subsequent government bond financing. Driven by special bonds and supporting loans, the intensity of infrastructure is expected to maintain, and new infrastructure is a more important lever. The situation where the growth rate of infrastructure in the broad sense is faster than that in the narrow sense may continue.
04 Jingtai Viewpoint | There may be a new round of reserve requirement reduction in the second half of the year. With the financial data performance in July significantly lower than market expectations, the market's expectations for future reserve requirement reduction and interest rate reduction have also increased. Based on the policy signals from recent major conferences, it is expected that the probability of a third quarter reserve requirement reduction and a fourth quarter interest rate reduction in the monetary policy dimension will be high. On the one hand, we will actively promote broad credit, improve the availability of corporate funds, and on the other hand, further promote the reduction of corporate financing costs. At the fiscal level, the urgency of central government deleveraging has increased to hedge against the decline in residents and businesses' willingness to leverage, while leading the improvement of real income expectations and confidence restoration, and promoting the benign repair of physical balance sheets. The acceleration of the subsequent issuance of special bonds and the potential release of refinancing local bond quotas are actually the logic of government leverage. However, if only the stock acceleration is achieved without new investment, it is difficult to completely reverse and restore physical confidence. The broad fiscal deficit may need further improvement to improve physical confidence. In addition to government leverage, it is also necessary to rely on the central bank's interest rate reduction to alleviate the weak growth rate of social finance, including further driving down mortgage rates and corporate financing costs, and stimulating endogenous financing demand through price incentives. The combination of stable finance and broad currency will be promoted in coordination, and the implementation of aggregate policies such as reducing reserve requirements is expected to accelerate. The issuance and use of government bonds will be accelerated, investment will be expanded, consumption will be promoted, and strong support will be given to technological innovation, the real economy, and the development of small and micro enterprises; The adjustment and optimization of real estate policies are accelerating, and the relaxation and structural optimization of purchasing policies in high-energy cities, as well as the construction of affordable housing and the transformation of urban villages, are expected to accelerate their implementation and take effect; Activating the capital market and promoting the formulation and implementation of a comprehensive debt restructuring plan all contribute to boosting investor confidence.